AI assistance in Technical writing
AI features are only as good as the content they rely on.
Why should we use AI-based agents?
Our base hypothesis is that AI-based systems can:
- Improve search in our developer documentation.
- Reduce the number of questions to our support organisation.
- Help improve the documentation by finding out what our customers ask about.
Chatbots have changed the way we search for information and answers to our questions. We no longer rely solely on search systems like Google Search. In addition, we use chatbots like ChatGPT, Co-pilot, Perplexity etc.
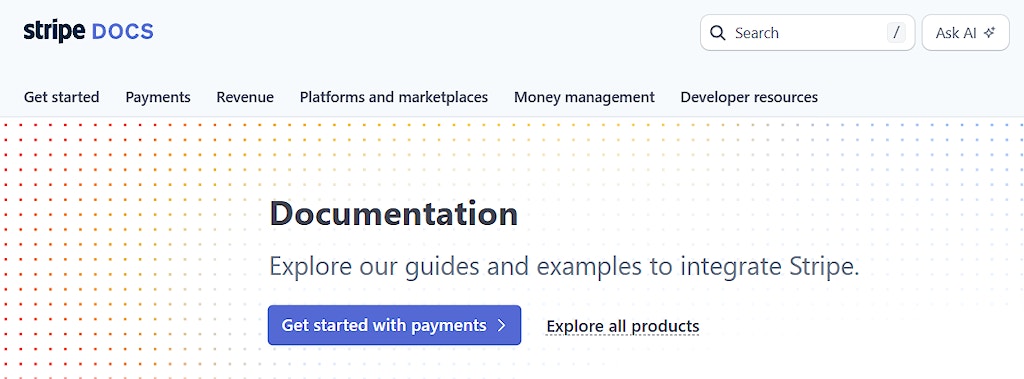
Many developer pages have now introduced AI assistants in their user interface. Some provide it as separate chatbots, and others as part of their regular search. Here is an example from Stripe where they have included an Ask AI button next to their Search button:
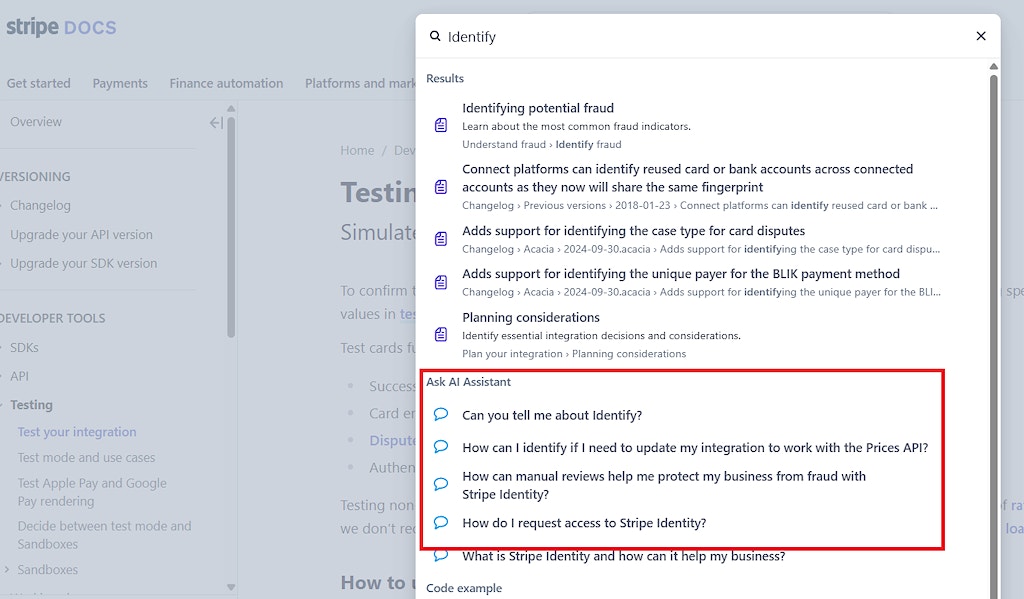
In addition, Stripe has integrated the AI assistant as part of their search. When entering a search term, you can see the traditional search hits on the top, but in addition, you get a list of suggested links under “Ask the AI Assistant” heading:
Why not?
AI assistants can offer additional help to our readers. However, we should also be aware of the main risks associated with AI assistants:
- Hallucination: AI assistants can generate inaccurate, misleading or even false information, leading to poor decision-making.
- Data privacy breaches: AI assistants can process and store sensitive personal data. Be sure that the suppliers you use, handle data securely.
- Fraud: Advanced AI assistants can be manipulated to generate deepfakes, clone voices, or create convincing fake identities, amplifying threats such as fraud or impersonation.
- Environment: Training AI assistants is resourceful.
Who reads our documentation?
Recent research (see for example DesignRush), has shown that bots now account for approximately 80% of all web traffic, meaning only about 20% of website visitors are real humans. For developer-focused pages, which often contain valuable technical content, the proportion of bot traffic may be even higher.
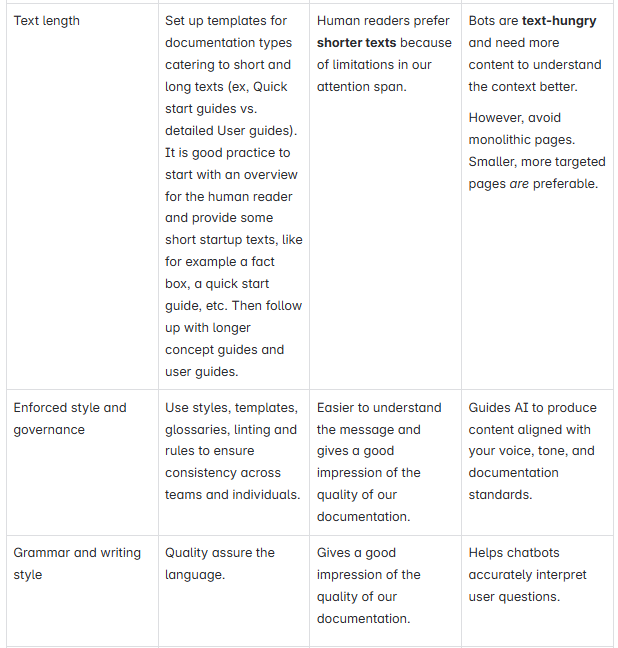
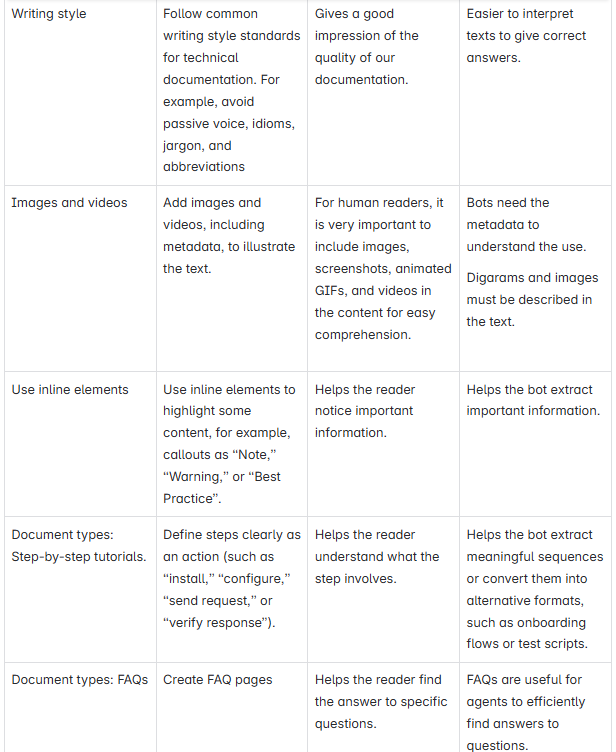
How should we write?
Successful AI-augmentations need clear, structured, and consistent content.
The good news is that you can mostly write for AI bots as you would for humans. However, there are still some minor differences. For example, LLMs are more text-hungry and need more text to understand the context better.
Awareness of the similarities and smaller differences will help us cater to both audiences.
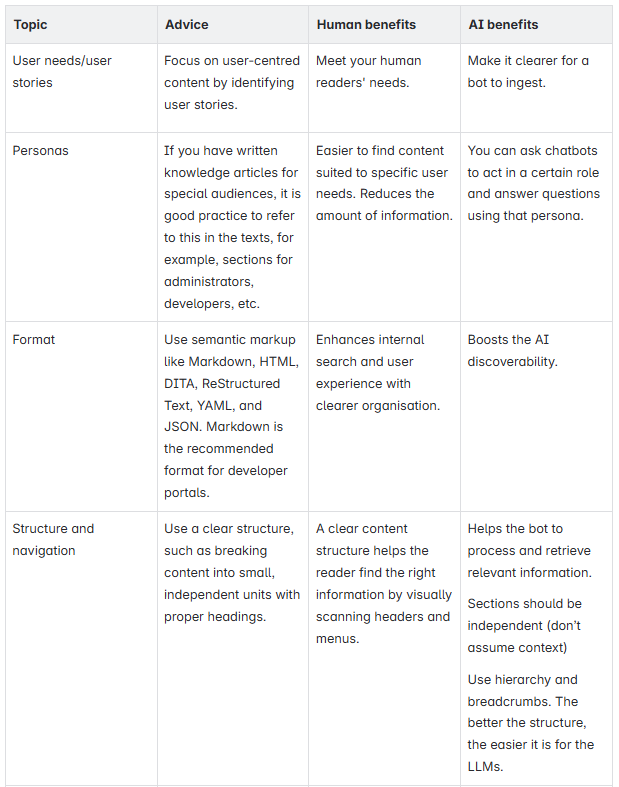
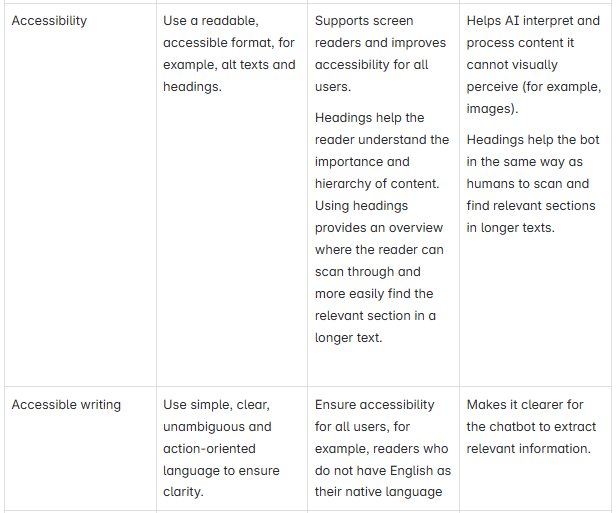
How to get started with an AI assistant?
The preferred option (if affordable) is to buy an AI assistant.
However, if you have internal AI experts, you could consider implementing it yourself. Below are some process steps for implementing an AI assistant.
Define the scope and main aim
- Guide developers through the developer documentation (addition or part of the search).
- Find out what customers ask about to improve our docs.
Understand user needs
Define personas.
Design the conversation flow
- Initial greeting and options.
- Handling specific developer queries.
- Escalate to human support.
- Fallback response for unknown questions.
Choose platform
Choose a platform that suits your infrastructure best. In Signicat, we use the Google Cloud platform and should look for solutions that build on top of this.
Build the knowledge base
- Populate the chatbot with relevant sources. Our developer pages are very suitable, since they are already public.
- Ensure that the chatbot differs between the different documentation versions (DTP and Enterprise) in its answers.
- Prepare and improve the knowledge base (see tips in the above section, “How should we write”).
Use Natural Language Processing
Help the chatbot understand queries and provide accurate responses.
Test and deploy
Test the chatbot with various questions, for example, complex technical questions.
Sources and links to more docs
- Knowledge Base Software
- AI success begins with a strong developer portal content strategy
- Using Genertive AI in Technical Writing
- AI the docs 2024 (online conference)
- AI the docs 2025 (online conference)
- How a holistic approach to user experience and technical writing can drive AI-readiness
- Will our next users be AI agents? The future of content delivery with Fabrice Lacroix, founder of Fluid Topics (podcast)
- Writing documentation for AI: best practices
